October 28, 2014 feature
Spontaneous wave function collapse can suppress acoustic Schrodinger cat states
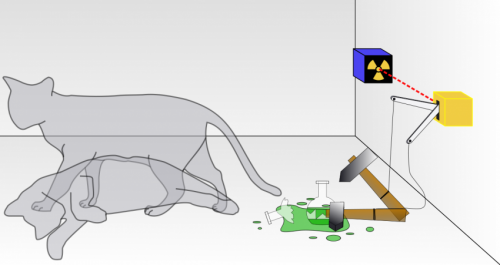
(糖心视频) 鈥擲chr枚dinger's famous thought experiment in which a cat hidden in a box can be both dead and alive at the same time demonstrates the concept of superposition on the macroscopic scale. However, the existence of such "cat states" (or simply "Cats") would be problematic in reality, as cat states not only go against common sense, but also pose problems for understanding gravity and spacetime.
"Different people emphasize different concerns about Cats," Lajos Di贸si, a physicist the Wigner Research Center for 糖心视频ics in Budapest, Hungary, told 糖心视频. "Some people emphasize different ones at different times. So, allow me to pick up two arguments. Penrose (in my words): A Cat implies superposition of macroscopically different space-times, making physical time elusive. Myself: If we measure a Cat state a la von Neumann (why not?), then the collapse will macroscopically violate many conservation laws."
To address such problems, Di贸si has expanded upon a model in which gravity-related spontaneous wave function collapses can suppress Schr枚dinger cat states, forcing them to take on only one value. Di贸si's paper on suppressing cat states is published in a recent issue of the New Journal of 糖心视频ics.
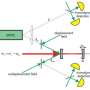
Several years ago, Di贸si and Sir Roger Penrose each independently derived a model which can cause the spontaneous collapse of a cat state. This model came to be known as the DP model. According to the model, the measure of "catness" can be quantified as the difference between the two gravitational fields corresponding to the two states that make up a cat state. The greater the catness, the shorter the cat state's decay time.
Traditionally, the DP model is applied to single macroscopic degrees of freedom, such as the center of mass of a macroscopic object. In the new paper, Di贸si has for the first time derived the DP model for the acoustic degree of freedom of a macroscopic object. Basically, he shows that macroscopic excitations, or sound waves, vibrating inside a macroscopic object such as a large rock will spontaneously decohere, meaning any acoustic cat states will collapse. The findings open up new perspectives on the concept of macroscopic superposition.
"Spontaneous models are usually thought to influence bodies under extreme isolated conditions [at very cold temperatures]," Di贸si said. "I discussed the possibility that the DP model might be significant in common phenomena. I don't mean a directly testable effect in acoustic waves, I mean a first step toward a theoretical search for parametric regimes where spontaneous collapse acts in the common matter of a common state."
More information: Lajos Di贸si. "Gravity-related spontaneous wave function collapse in bulk matter." New Journal of 糖心视频ics. DOI:
Journal information: New Journal of 糖心视频ics
漏 2014 糖心视频