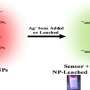
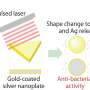
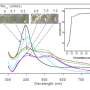
The synthesis procedure of AgNPs@rGO and its application in antibacterial effect. Credit: Liu Chao
Researchers from the Hefei Institutes of ������Ƶical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a novel approach of green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and reduced graphene oxide composite material (AgNPs@rGO) based on plasma technology.
This composite nanomaterial, according to the researchers, with much simplified manufacturing process, can be made into band-aids for wound sterilization and healing.
Abuse of antibiotics can cause bacterial resistance. Silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) have excellent antibacterial properties and biocompatibility, and introduction of the two-dimensional material graphene can greatly improve dispersibility of the silver nanoparticles and improve the sterilization efficiency. However, the current preparation methods of AgNPs@rGO composite usually require harsh conditions such as using toxic and polluting chemical reagents.
In this research, the researchers employed high-voltage direct-current discharge plasma for fabrication of AgNPs@rGO by reducing both Ag+ ions and graphene oxide simultaneously.
"The advantage is obvious, and it's ready for application," said Prof. Huang Qing, who led the research team, "this electrical flash strategy for synthesis of AgNPs@rGO composite nanomaterial took only a very short period time (within one minute), which is different from traditional high-cost and time-consuming processing."
The as-fabricated AgNPs@rGO nanomaterial showed excellent disinfection effect and bio-compatibility, and could be used for wound healing band-aids, as demonstrated by the researchers.
More information: Chao Liu et al, Single-step synthesis of AgNPs@rGO composite by e-beam from DC-plasma for wound-healing band-aids, Chemical Engineering Journal Advances (2021).
Provided by Chinese Academy of Sciences