Climate change is making flooding worse: 3 reasons the world is seeing more record-breaking deluges

Heavy rain combined with melting snow can be a destructive combination.
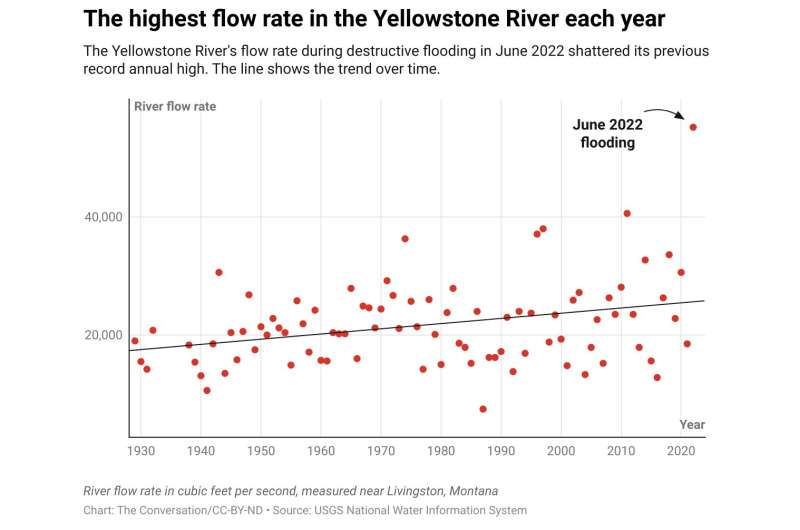
In mid-June 2022, storms dumped up to 5 inches of rain over three days in the mountains in and around Yellowstone National Park, rapidly melting snowpack. As the rain and meltwater poured into creeks and then rivers, it became a flood that damaged roads, cabins and utilities and .
The Yellowstone River shattered its previous record and reached its highest water levels recorded since monitoring began almost 100 years ago.
Although floods are a natural occurrence, human-caused climate change is . I study how climate change affects hydrology and flooding. In mountainous regions, three effects of climate change in particular are creating higher flood risks: more intense precipitation, shifting snow and rain patterns and the effects of wildfires on the landscape.
Warmer air leads to more intense precipitation
One effect of climate change is that a .
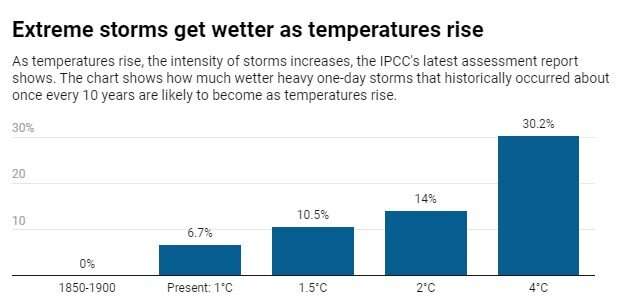
This occurs because warmer air can hold more moisture. The amount of water vapor that the atmosphere can contain increases by (1 degree Celsius) of increase in atmospheric temperature.
Research has documented that this , not only in regions like Yellowstone, but around the globe. The fact that the world has experienced multiple record flooding events in recent years—including catastrophic , and —is not a coincidence. Climate change is making record-breaking extreme precipitation more likely.
The latest published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change shows how this pattern will continue in the future as global temperatures continue to rise.
More rain, less snow
In colder areas, especially mountainous or high-latitude regions, climate change affects flooding in additional ways.
In these regions, many of the largest historical . However, with warmer winters due to climate change, , and more is falling as rain instead.
This shift from snow to rain can have dramatic implications for flooding. While snow typically melts slowly in the late spring or summer, rain creates runoff that flows to rivers more quickly. As a result, research has shown that , and that the shift from snow to rain .
The transition from snow to rain is already occurring, including in places like Yellowstone National Park. Scientists have also found that . In some locations, the changes in flood risk due to the shift from snow to rain could even be larger than the effect from increased precipitation intensity.
Changing patterns of rain on snow
When , as happened in the recent flooding in Yellowstone, the combination of rain and snowmelt can lead to especially high runoff and flooding.
In some cases, rain-on-snow events occur while the ground is still partially frozen. Soil that is frozen or already saturated can't absorb additional water, so even more of the rain and snowmelt run off, contributing directly to flooding. This combination of rain, snowmelt and frozen soils was a primary driver of the that caused over US$12 billion in damage.
While rain-on-snow events are not a new phenomenon, climate change can shift when and where they occur. Under warmer conditions, , where they were previously rare. Because of the increases in rainfall intensity and warmer conditions that lead to rapid snowmelt, there is also the possibility of larger rain-on-snow events than these areas have experienced in the past.
In lower-elevation regions, rain-on-snow events may actually become less likely than they have been in the past because of the decrease in snow cover. These areas could still see worsening flood risk, though, because of the increase in heavy downpours.
Compounding effects of wildfire and flooding
Changes in flooding are not happening in isolation. Climate change is also exacerbating , creating another risk during rainstorms: mudslides.
Burned areas are more , both because of the lack of vegetation and changes to the soil caused by the fire. In 2018 in Southern California, heavy rain within the boundary of the caused that destroyed over 100 homes and led to more than 20 deaths. Fire can change the soil in ways that allow , so more rain ends up in streams and rivers, leading to worse flood conditions.
With the uptick in wildfires due to climate change, more and more areas are exposed to these risks. This combination of wildfires followed by extreme rain will also become .
Global warming is creating complex changes in our environment, and there is a clear picture that it increases flood risk. As the Yellowstone area and other flood-damaged mountain communities rebuild, they will have to find ways to adapt for a riskier future.
Provided by The Conversation
This article is republished from under a Creative Commons license. Read the .![]()



















