Volcanic fallout from Taupō eruption 1,800 years ago found in Antarctic ice core

Volcanic debris from the massive Taupō eruption about 1,800 years ago has been found buried deep in Antarctic ice, according to a published in Scientific Reports.
Scientists have been hunting for evidence of the eruption for more than a decade, hoping it would help pin down the date of this event, which has been a point of dispute, said Stephen Piva, the study's lead author and a Ph.D. candidate at Te Herenga Waka—Victoria University of Wellington.
"The Taupō eruption was one of the largest and most powerful volcanic eruptions known to have occurred in the past 5,000 years, devastating an area of about 20,000 kilometers and spreading volcanic fallout throughout the region.
"But exactly when the eruption occurred has sparked debate. Our discovery of seven geochemically unique volcanic glass shards buried deep within an ice core confirms the likely timing of the eruption in late summer/early autumn in the year 232," he said.
The volcanic glass shards were found at a depth of 279 meters in the Roosevelt Island Climate Evolution ice core, taken from West Antarctica.
Analysis of the geochemical make-up of the shards linked them to the Taupō eruption. Researchers were then able to assess how long the shards had been there based on the modeled age of the ice layers.
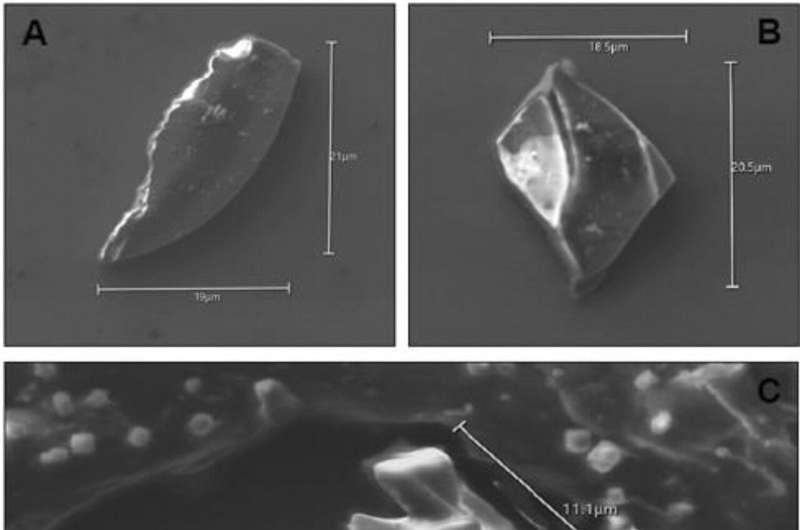
"Ice cores provide invaluable records of the past. Finding and fingerprinting volcanic debris trapped in the ice allows us to date when the eruption occurred because we can link it to the modeled age of the ice," Mr. Piva said.
Of the seven shards, one was a match for volcanic glass produced by the earlier Ōruanui supereruption of the Taupō volcano. Mr. Piva said this glass would have been unearthed when Taupō erupted again in 232 with fragments finding their way to Antarctica.
The other six shards had a similar geochemical composition that researchers considered could be confidently linked to the Taupō eruption itself.
"Combined, the seven shards provide a unique and undeniable double fingerprint of the Taupō volcano as the source," he said.
Detecting the glass shards in Antarctica, which is about 5,000 km away from Taupō, shows the power of the eruption.
"A massive eruption plume would have sent a huge volume of volcanic particles into the air where they would have been widely dispersed by the wind. Confirming the eruption date provides an opportunity to study the volcano's potential global effects on the atmosphere and climate, which is crucial for better understanding its eruptive history and behavior."
More information: Stephen B. Piva et al, Volcanic glass from the 1.8 ka Taupō eruption (New Zealand) detected in Antarctic ice at ~ 230 CE, Scientific Reports (2023).
Journal information: Scientific Reports
Provided by Victoria University of Wellington



















