3D-printed living cells pave way for tomorrow's medicine and cruelty-free animal products
Researchers are expanding the possibilities of 3D printing to create miniature human organs and a variety of products made from living tissue, including food.
See also stories tagged with Regenerative medicine

Researchers are expanding the possibilities of 3D printing to create miniature human organs and a variety of products made from living tissue, including food.

Communication and coordination among different cells are fundamental aspects that regulate many functions in our body. This process, known as paracrine signaling, involves the release of signaling molecules by a cell into ...

A research team at the Technical University of Denmark, led by Alireza Dolatshahi-Pirouz, has recently made strides in tissue engineering and cell therapy by harnessing the healing power of bacteria.
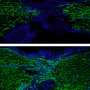
Zebrafish are members of a rarefied group of vertebrates capable of fully healing a severed spinal cord. A clear understanding of how this regeneration takes place could provide clues toward strategies for healing spinal ...

How similar is kidney development in humans and in the lab mice that form the foundation of basic medical research? In a study published in Developmental Cell, USC Stem Cell scientists probe this question by comparing the ...
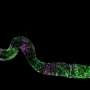
A team of researchers, including colleagues from the University of Tokyo's Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, have transferred into common fruit flies genes from simple organisms capable of regenerating their bodies. ...

Terasaki Institute scientists have created a nature-inspired cutting-edge technology by developing a novel bioink derived from egg whites or egg white methacryloyl (EWMA). A paper describing their work is published in the ...
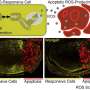
A new study published in The EMBO Journal opens new perspectives to better understand how the molecular mechanisms involved in regenerative medicine work.
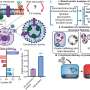
Each cell in the body has its own unique delivery system that scientists are working on harnessing to move revolutionary biological drugs鈥攎olecules like proteins, RNA and combinations of the two鈥攖o specific diseased parts ...

Researchers at Tel Aviv University relied on principles of origami, the Japanese art of paper folding, to develop an original and innovative solution for a problem troubling researchers worldwide: positioning sensors inside ...